6 Page Quick Short Notes On APQP
I have taken some quick short notes for APQP while preparing for TS16949 IATF Auditor Evaluation process. Sharing this to my followers, as it may be useful for someone. I will share other short notes i have taken on core tools one by one.
Thanks for
spending your valuable time here. Keep in touch, keep following & keep
supporting us.
Thanks
& Regards,
Devarajan NR,
Chairman – JBEGlobal.com Job Portal & IATFTrainingPortal.com (Since 2013) Past – Delphi TVS | Rane | Brakes India |
Iris Mfg. (Shriram Group) | Hinduja Foundries | IRS (IRQS) | 9362439124 | devarajan.jupiter@gmail.com
Advanced product quality planning & control plan (APQP)
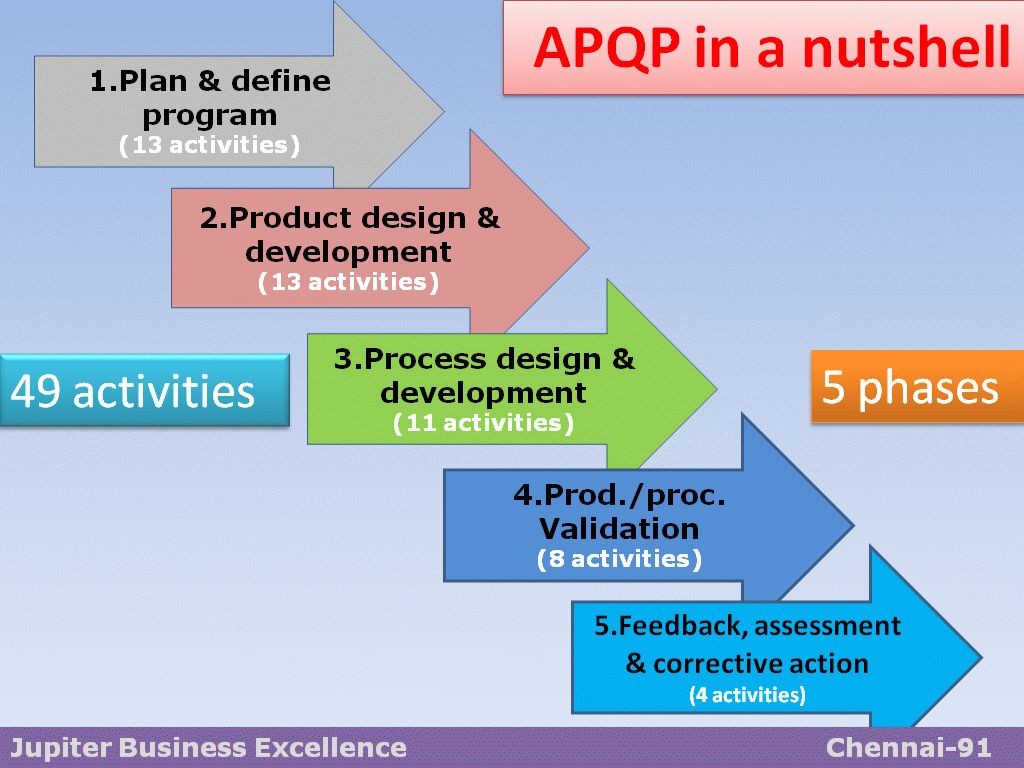
Before getting into the short notes please see this nutshell which will be helpful in understanding APQP better.
Introduction
1. Provides guidelines designed to produce a quality plan, which will support the development of a product or service that will satisfy customer.
2. Product quality planning responsibility matrix,
a) Design responsible organizations have responsibility to follow all eight (8) activities.
b) Mfg. only & Service organizations have responsibility to follow six (6) activities.
3. Fundamentals of product quality planning,
a) Structured method of defining & establishing the steps necessary to assure that a product satisfies the customer.
b) Benefits are,
i. Direct resources to satisfy customer
ii. Promote early identification of required changes
iii. Avoid late changes
iv. Right product at right time at right cost
c) Organize the team – Assign process owner & establish team
d) Define the scope
e) Team to team – regular meetings with other teams depending upon the number of issues requiring resolution.
f) Training
g) Customer & organization involvement – organizations to expect same performance from their suppliers.
h) Simultaneous engineering – replaces sequential series of phases
i) Control plan – written description of the systems for controlling parts & processes
j) Concern resolution – product / process concerns should be documented on a matrix with assigned responsibility & timing. Disciplined problem solving methods are recommended in difficult situations.
k) Product quality timing plan
l) Plans relative to the timing chart
1-Plan & define program
1. Introduction – aims to ensure customer needs & expectations are clearly understood
2. Inputs,
a) Voice of the customer
i. Market research (customer interviews, customer questionnaires & surveys, market test & positioning reports, new product quality & reliability studies, competitive product quality studies, best practices and lessons learned)
ii. Historical warranty & quality information (best practices, lessons learned, warranty report, capability indicators, internal quality reports, problem resolution reports, customer returns & rejections, field return product analysis)
iii. Team experience (customer letters & suggestions, best practices, lessons learned, dealer comments, fleet operator’s comments, field service reports, internal evaluations using surrogate customers, road trips, management comments or direction, problems & issues reported from internal customers, Govt. requirements & regulations, contract review)
b) Business plan / marketing strategy (timing, cost, investment, product positioning, R&D resources, target customers, key sales points, key competitors)
c) Product / process benchmark data
d) Product / process assumptions (technical innovations, advanced materials, reliability assessments & new technology)
e) Product reliability studies (frequency of repair or replacement)
f) Customer inputs (next users of the product)
3. Outputs, (become inputs for chapter-2)
g) Design goals (translating voice of the customer into measurable design objectives)
h) Reliability & quality goals (established based on customer wants & expectations, program objectives & reliability benchmarks)
i) Preliminary bill of material
j) Preliminary process flow chart
k) Preliminary listing of special product & process characteristics
l) Product assurance plan
m) Management support
2-Product design & development
1. Introduction – design features & characteristics are developed into a near final form.
2. Design outputs, (become inputs for chapter-3)
a) DFMEA
b) Design for manufacturability & assembly
c) Design verification
d) Design reviews
e) Prototype build – control plan
f) Engineering drawings (including math data)
g) Engineering specifications
h) Material specifications
i) Drawing & specification changes
3. APQP outputs,
a) New equipment, tooling & facilities requirements
b) Special product & process characteristics
c) Gages / testing equipment requirements
d) TFC & Management support
3-Process design & development
1. Introduction
2. Outputs, (become inputs for chapter-4)
a) Packaging standards & specifications
b) Product / process quality system review
c) Process flow chart
d) Floor plan layout (inspection points, control chart location, applicability of visual aids, interim repair stations, NC storage areas)
e) Characteristics matrix
f) PFMEA
g) Pre-launch control plan
h) Process instructions
i) MSA plan
j) Preliminary process capability plan
k) Management support (including operator staffing & training plan)
4-Product & process validation
1. Introduction – validating the manufacturing process thro an evaluation of a significant production run
2. Outputs, (become inputs for chapter-5)
a) Significant production run
b) Measurement systems evaluation
c) Preliminary process capability study
d) Production part approval
e) Production validation testing
f) Packaging evaluation
g) Production control plan
h) Quality planning sign-off (completes APQP activities) & management support
5-Feedback, assessment & corrective action
1. Introduction
2. Outputs,
a) Reduced variation
b) Improved customer satisfaction
c) Improved delivery & service
d) Effective use of lessons learnt / best practices
6-Control plan methodology
1. Introduction
a) Benefits,
i. Quality
ii. Customer satisfaction
iii. Communication
2. Process analysis,
a) Examples are,
i. Fault tree analysis
ii. Design of experiments
iii. Cause & effect
3. Supplements (control plan samples),
a) Supplement-A – Set-up dominant process
b) Supplement-B – Machine dominant process
c) Supplement-C – Fixture / pallet dominant process
d) Supplement-D1 – Tooling dominant process
e) Supplement-D2 - Tooling dominant process
f) Supplement-E – Operator dominant process
g) Supplement-F – Material or component dominant process
h) Supplement-G – Preventive maintenance dominant process
i) Supplement-H – Climate dominant process
j) Supplement-I – Control plan blank format
k) Supplement-J – Control plan check list
l) Supplement-K – Control plan special characteristic (with data point co-ordinates – optional)
Appendix-A – Product quality planning checklists
1. Purpose
2. Check lists,
a) A-1 Design FMEA checklists
b) A-2 Design information checklist
c) A-3 New equipment, tooling & test equipment checklist
d) A-4 Product / process quality checklist
e) A-5 Floor plan checklist
f) A-6 Process flow chart checklist
g) A-7 Process FMEA checklist
h) A-8 Control plan checklist
Appendix-B – Analytical techniques
1. Following techniques are discussed,
a) Assembly build variation analysis – simulates build-up of an assembly & examines tolerance accumulation, statistical parameters, sensitivity, & “what if” investigation.
b) Benchmarking – world class or best in class research into how this performance was achieved.
c) Cause & effect diagram – referred as fishbone, ishikawa or feather diagram.
d) Characteristics matrix – display of the relationship between process parameters & mfg. stations. Number dimensions on print & relate to mfg. operation.
e) Critical path method – PERT or Gantt chart showing chronological sequence of tasks.
f) Design of experiments (DOE) – test or sequence of tests to find effects of influential process variables.
g) Design for manufacturability & assembly – simultaneous engineering process designed to optimize the relationship between design function, manufacturability & ease of assembly.
h) Design verification plan & report (DVP&R) – method to plan & document testing activity through each phase of product / process development from inception to ongoing refinement.
i) Mistake proofing / error proofing – mistake proofing is detection & error proofing is prevention.
j) Process flow charting – visual approach to describing & developing sequential or related work activities.
k) Quality function deployment – procedure for translating customer requirements into technical & operational terms.
Appendix-C – Reference material
1. MSA, FMEA, PPAP, SPC
Appendix-D – Team feasibility commitment
Appendix-E – Product quality planning summary & approvals
Appendix-F – Glossary
1. Following definitions given,
a) Apportionment (in this manual) - assignment of reliability goals from system to sub-system in such a way that the whole system will have the required reliability.
b) Benchmark data – to determine how best-in-class performance is achieved.
c) Bill of material – list of components / materials to manufacture a product.
d) Characteristics matrix – display relationship between process parameters Vs mfg. stations.
e) DFMEA
f) Design for manufacturability & assembly – optimizes relationship between design function, manufacturability & ease of assembly.
g) Design information checklist – a mistake proofing checklist designed to assure that all important items were considered in establishing design requirements.
h) Design reviews – milestone checkpoints to review progress proactively.
i) Design validation – confirmation through objective evidence on intended use have been fulfilled.
j) Design verification – confirmation through objective evidence, that specific requirements have been fulfilled.
k) Durability – Probability that an item will continue to function at expected levels without overhaul or rebuild.
l) FMEA
m) Feasibility – A determination of success w.r.t process, design, procedure or plan.
n) Packaging – protection & containment with ease of handling.
o) Pass through characteristics – parts received from supplier used as it is (no modification or validation).
p) Preliminary bill of material – completed prior to design & print release.
q) Preliminary process flow chart – early depiction of the anticipated mfg.process for a product.
r) PFMEA
s) Product assurance plan – A part of product quality plan. It is a prevention oriented management tool that addresses product design, process design, & when applicable software design.
t) Quality planning approval – a review & verification that all planned controls & processes are being followed.
u) Reliability – the probability that an item will continue to function at customer expectation levels at a measurement point, under specified environmental & duty cycle conditions.
v) Reliability apportionment – See apportionment (sl.no.1).
w) Significant production run – product made using all production tools, processes, equipment, environment, facility & cycle time.
x) Simulation – imitating some or all the behavior of one system with a different, dissimilar system.
y) Special characteristics – characteristics having significant impact on the quality, function, fit, safety – designated by customer or selected by organization through knowledge of product & process.
z) Subsystem – a major part of a system which itself has the characteristics of a system, usually consisting of several components or processes.
aa) System – a combination of several components, processes or pieces of equipment integrated to perform a specific function.
bb) Team feasibility commitment – team commitment on manufacturability & delivery of a product at required rate & cost.
cc) Timing plan – listing of tasks, assignments, events & timing required to provide a product that meets customer needs & expectations.
dd) Voice of the customer – Positive & negative feedback of customers including likes, dislikes, problems & suggestions.