I have taken some quick short notes while preparing for TS16949 IATF Auditor Evaluation process. Sharing this to my followers, as it may be useful for someone. I will share other short notes i have taken on core tools one by one.
Keep in touch & keep following.
Thanks!
Thanks & Regards,
Devarajan NR,
Chairman – JBEGlobal.com Job Portal & IATFTrainingPortal.com (Since 2013)
Past – Delphi TVS | Rane | Brakes India | Iris Mfg. (Shriram Group) | Hinduja Foundries | IRS (IRQS)
9362439124 | devarajan.jupiter@gmail.com
========== ==========
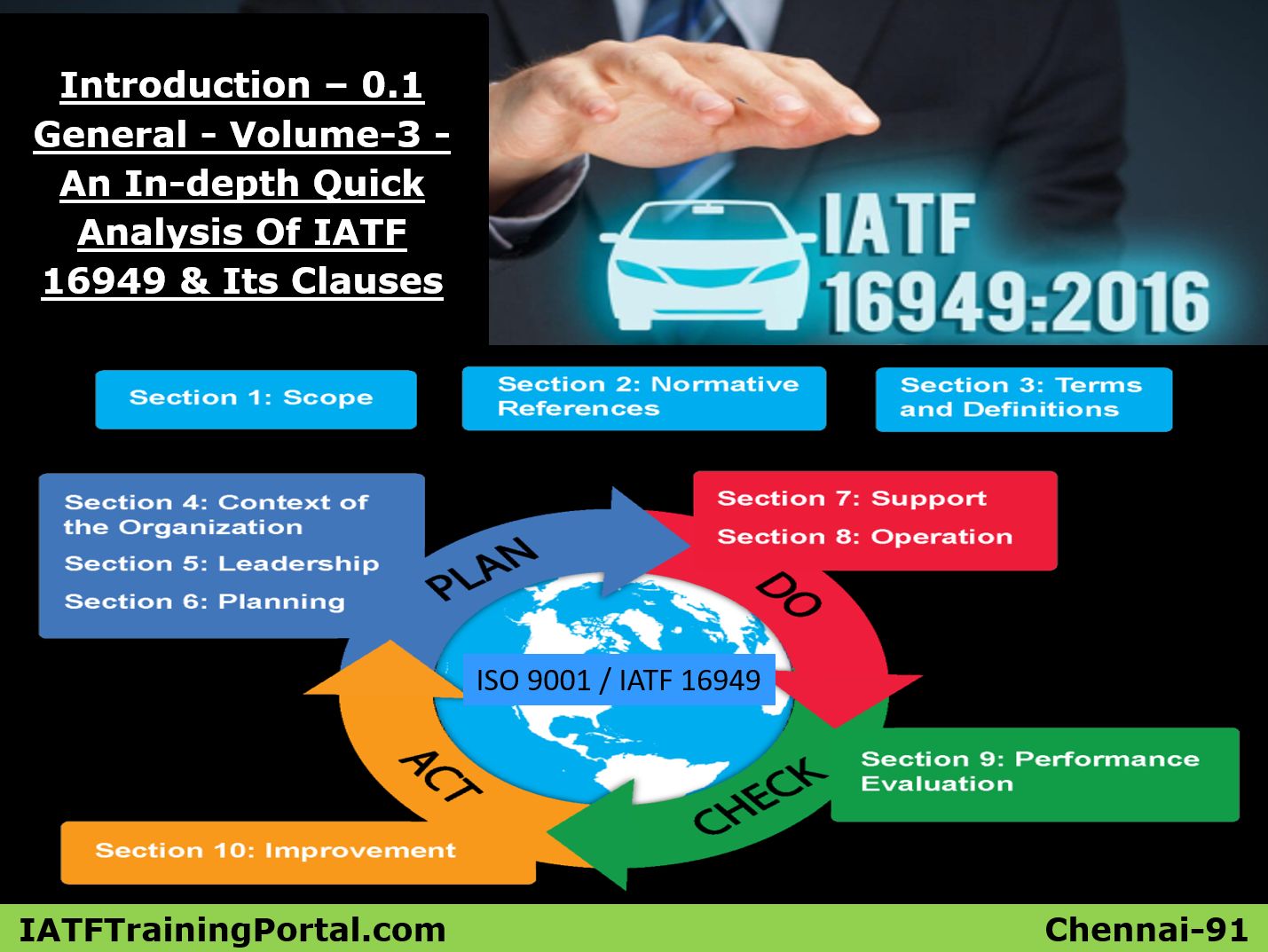
TS 16949 requirements
General
- The work of preparing international standards is normally carried out through ISO technical committees
- ISO collaborates closely with the International Electro-technical Commission (IEC) on all matters of electro-technical standardization
- International standards are drafted in accordance with the rules given in the ISO/IEC Directives, Part 2
- Publication as an international standard requires approval by atleast 75% of the member bodies casting a vote (ISO/PAS-50%, ISO/TS-66%)
- ISO/TS16949 was prepared by the IATF, with the support from ISO/TC 176, quality management & quality assurance committee.
- Boxed text is original ISO 9001:2008 text. Sector specific supplemental requirements are outside the boxes
- “Shall” indicates a requirement. “Should” indicates a recommendation. “Note” is for guidance in understanding or clarifying the associated requirement. “Such as” are suggestions given for guidance only.
- Annex-A forms normative part
- TS requirements are complementary to requirements for products
- The quality management principles stated in ISO 9000 & ISO 9004 have been taken into consideration during the development of TS standard
- Promotes the adoption of a process approach (An activity or set of activities using resources, & managed in order to enable the transformation of inputs into outputs, can be considered as a process), which emphasizes the importance of,Understanding & meeting requirements
- The need to consider processes in terms of added value
- Obtaining results of process performance & effectiveness and
- Continual improvement of processes based on objective measurement
- ISO 9001 & ISO 9004 are quality management system standards which have been designed to complement each other, but can also be used independently. ISO 9004 will provide guidance to management for achieving sustained success.
- Knowledge & use of eight quality management principles should be demonstrated & cascaded through the organization by top management.
- Due consideration was given to enhance the compatibility with other management systems (environment, health & safety, financial, risk), but does not include requirements specific to other management systems.
- Goal of this technical specification,Continual improvement
- Emphasizing defect prevention and
- Reduction of variation & waste in supply chain
- TS coupled with applicable customer specific requirements defines the fundamental QMS requirements
- In TS product applies to,Product intended for or required by a customer
- Any intended output resulting from the product realization process
- TS is applicable to sites where customer specified parts, for production and / or service, are manufactured
- Supporting functions whether on-site or remote form part of the site audit, but cannot obtain stand alone certification
- TS can be applied throughout the automotive supply chain
- Permitted exclusions relate to 7.3-Product design & development (that too when seen in spirit, 7.3.2.1-Product design input & 7.3.3.1-Product design outputs supplemental only can be excluded)
- ISO 9000:2005 – QMS fundamentals & vocabulary is the normative reference which is indispensable for the application of TS
- Throughout TS standard, term “product” can also mean “service”
- Twelve (12) Terms & definitions for automotive industry defined (control plan, design responsible organization, error proofing, laboratory, laboratory scope, manufacturing, predictive maintenance, preventive maintenance, premium freight, remote location, site & special characteristic)
Documented procedures (mandatory)
- (4.2.3) – Control of documents
- (4.2.4) – Control of records
- (6.2.2.2) – Training
- (8.2.2) – Internal audit
- (8.3) – Control of NC product
- (8.5.2) – Corrective action
- (8.5.3) – Preventive action
Top management
- Provide evidence of its commitment to the development and implementation of the QMS & continually improving its effectiveness by,Communicating the importance of meeting customer as well as statutory & regulatory requirements
- Establishing the quality policy
- Ensuring that quality objectives are established
- Conducting management reviews and
- Ensuring availability of resources
- Review the product realization processes & the support processes to assure their effectiveness & efficiency
- Ensure that customer requirements are determined & are met with the aim of enhancing customer satisfaction
- Ensure that the quality policy,Is appropriate to the purpose of the organization,
- Includes a commitment to comply with the requirements & continually improve the effectiveness of the QMS,
- Provides a framework for establishing & reviewing quality objectives,
- Is communicated & understood within the organization and
- Is reviewed for continuing suitability.
- Ensure quality objectives, including those needed to meet requirements for product, are established at relevant functions & levels within the organization. Define quality objectives & measurements that shall be included in the business plan & used to deploy quality policy.
- Ensure that,The planning of QMS is carried out in order to meet the requirements given in 4.1 (general requirements), as well as the quality objectives, and
- The integrity of the quality management system is maintained when changes to the QMS are planned & implemented.
- Ensure that responsibilities & authorities are defined & communicated within the organization.
- Appoint a member of the organisation’s management as “Management representative”. Designate a “Customer representative”.
- Ensure that appropriate communication processes are established within the organization & that communication takes place regarding the effectiveness of the QMS.
- Review the organisation’s QMS at planned intervals, to ensure its continuing suitability, adequacy & effectiveness.
Management representative
- Ensuring that processes needed for the QMS are established, implemented & maintained,
- Reporting to top management on the performance of QMS & any need for improvement, and
- Ensuring promotion of awareness of customer requirements throughout the organization
- Liaison with external parties on matters relating to the QMS
Customer representative
- Selection of special characteristics
- Setting quality objectives & related training
- CAPA
- Product design & development
Processes to be established
- 1 – General requirements – determine the processes needed for the quality management system & their application throughout the organization.(5.5.3) – Internal communication – Top management shall ensure that appropriate communication processes are established within the organization & that communication takes place regarding the effectiveness of the QMS
- (6.2.2.4) – Employee motivation & empowerment >>The organization shall have a process to motivate employees to achieve quality objectives, to make continual improvements, & to create an environment to promote innovation. The process shall include the promotion of quality & technological awareness throughout the whole organization. >>The organization shall have a process to measure the extent to which its personnel are aware of the relevance & importance of their activities & how they contribute to the achievement of the quality objectives.
- (7.1) – Planning of product realization – The organization shall plan & develop the processes needed for product realization. Planning of product realization shall be consistent with the requirements of the other processes of the QMS.
- (7.1.4) – Change control – The organization shall have a process to control & react to changes that impact product realization.
- (7.4.3.1) – Incoming product conformity to requirements – The organization shall have a process to assure the quality of purchased product utilizing one or more of the following methods,Receipt of, & evaluation of, statistical data by the organization
- Receiving inspection and/or testing, such as sampling based on performance
- Second or third party assessments or audits of supplier sites, when coupled with records of acceptable delivered product conformity to requirements
- Part evaluation by a designated laboratory
- Another method agreed with the customer
- (7.5.1.7) – Feedback of information from service – A process for communication of information on service concerns to manufacturing, engineering & design activities shall be established & maintained.
- (7.6) – Control of monitoring & measuring equipment – The organization shall establish processes to ensure that monitoring & measurement can be carried out & are carried out in a manner that is consistent with the monitoring & measurement requirements.
- (8.1) – Measurement, analysis & improvement – General – The organization shall plan & implement the monitoring, measurement, analysis & improvement processes (SPC) needed,To demonstrate conformity to product requirements
- To ensure conformity of the QMS and
- To continually improve the effectiveness of the QMS
- (8.5.1.1) – Continual improvement of the organization – The organization shall define a process for continual improvement.
- (8.5.2.1) – Problem solving – The organization shall have a defined process for problem solving leading to root cause identification & elimination.
Time limits
- (4.2.3.1) - Engineering specifications – timely review should be as soon as possible, and shall not exceed two working weeks.
- (8.2.2) – Internal audits – The management responsible for the area being audited shall ensure that necessary corrections & corrective actions are taken without undue delay to eliminate detected non-conformities & their causes.
- (8.5.2.4) – Rejected product/test analysis – The organization shall minimize the cycle time of this process.
Multi disciplinary approach
- Prepare for product realization (APQP),
- Development, finalization & monitoring of special characteristics,
- Development & review of FMEA, including actions to reduce potential risks,
- Development & review of control plans,
- Developing plant, facility & equipment
Management review inputs
- All Performance trends of QMS
- Monitoring of quality objectives (asper business plan or asper quality manual)
- Cost of poor quality
- Results of audits
- Customer feedback (Customer score cards, self assessment on customer satisfaction, complaints, line rejection & other information)
- Process performance & product conformity
- Status of preventive & corrective actions
- Follow up actions from previous management reviews
- Changes that could affect the QMS
- Recommendations for improvement
- Analysis of actual & potential field failures & their impact on quality, safety or the environment
- Design & development progress (Measurements at specified stages of design and development shall be defined, analysed and reported with summary results as an input to management review. Egs: quality risks, costs, lead times, critical paths)
- Need for changes to the qms including quality policy & quality objectives
Monitor / Measure / Indicators
- (7.4.3.2) – Supplier monitoring – Supplier performance shall be monitored through the following indicators:Delivered product conformity to requirements
- Customer disruptions, including field returns
- Delivery schedule performance (including incidents of premium freight) and
- Special status customer notifications related to quality or delivery issues.
- (8.2.1.1) – Customer satisfaction – supplemental – Customer satisfaction with the organization shall be monitored through continual evaluation of performance of the realization process. Performance indicators shall be based on objective data and include, but not be limited to:Delivered part quality performance
- Customer disruptions, including field returns
- Delivery schedule performance (including incidents of premium freight) and
- Customer notifications related to quality or delivery issues.
- (5.6.1.1) – QMS performance – Evaluation of the cost of poor quality
- (6.3.1) – Plant, facility & equipment planning – Methods shall be developed & implemented to evaluate & monitor the effectiveness of the existing operations.
- (4.1) – General requirements – Monitor, measure where applicable & analyze these processes.
- (5.4.1.1) – Quality objectives – supplemental – Quality objectives & measurements that shall be included in the business plan & used to deploy the quality policy
- (6.2.2.4) – Employee motivation & empowerment – Measure the extent to which its personnel are aware of the relevance & importance of their activities & how they contribute to the achievement of the quality objectives.
- (7.3.4.1) – Monitoring – Measurements at specified stages of design & development shall be defined, analysed & reported with summary results as an input to management review.
- (8.2.3.1) – Monitoring & measurement of manufacturing processes – The organization shall ensure that the control plan & process flow diagram are implemented, including adherence to the specified,Measurement techniques
- Sampling plans
- Acceptance criteria and
- Reaction plans when acceptance criteria are not met.
- (8.2.4) – Monitoring & measurement of product – The organization shall monitor & measure the characteristics of the product to verify that product requirements have been met. This shall be carried out at appropriate stages of the product realization process in accordance with the planned arrangements.
Competency (Education, skills, experience)
- (6.2.1) – HR – General – Personnel performing work affecting conformity to product requirements shall be competent on the basis of appropriate education, training, skills & experience
- (6.2.2) – Competence, training & awareness – The organization shall (a) determine the necessary competence for personnel performing work affecting conformity to product requirements, (b) where applicable, provide training or take other actions to achieve the necessary competence …..
- (6.2.2.1) – Product design skills – The organization shall ensure that personnel with product design responsibility are competent to achieve design requirements & are skilled in applicable tools & techniques.
- (7.6.3.1) – Internal laboratory – The laboratory shall specify & implement, as a minimum, technical requirements for… (b)competency of the laboratory personnel
Qualifications
- (6.2.2.2) – Training – Personnel performing specific assigned tasks shall be qualified, as required, with particular attention to the satisfaction of customer requirements.
- (7.5.2) – Validation of processes for production & service provision – The organization shall establish arrangements for these processes including, as applicable … (b) approval of equipment & qualification of personnel
- (8.2.2.5) – Internal auditor qualification – The organization shall have internal auditors who are qualified to audit the requirements of technical specification.
Validations
- (7.1.4) – Change control – Changes shall be validated before implementation.
- (7.3.6) – Design & development validation – Design & development validation shall be performed in accordance with planned arrangements to ensure that the resulting product is capable of meeting the requirements for the specified application or intended use, where known. Wherever practicable, validation shall be completed prior to the delivery or implementation of the product. Records of the results of validation and any necessary actions shall be maintained.
- (7.3.7) – Control of design & development changes – The changes shall be reviewed, verified & validated, as appropriate & approved before implementation.
- (7.5.2) – Validation of processes for production & service provision – All processes for production & service provision shall be validated. The organization shall establish arrangements for these processes including, as applicable,Defined criteria for review & approval of the processes,
- Approval of equipment & qualification of personnel,
- Use of specific methods & procedures,
- Requirements for records and
- revalidation
Documents / Records
- (4.2.1) – Documentation requirements – General – QMS documentation shall include,Documented statements of quality policy & quality objectives
- A quality manual
- Documented procedures & records required by TS standard
- Documents, including records, determined by the organization to be necessary to ensure the effective planning, operation & control of its processes.
- (4.2.3.1) - Engineering specifications – organization shall maintain a record of the date on which each change is implemented in production
- (5.4.1.1) – Quality objectives – supplemental – Top management shall define quality objectives & measurements that shall be included in the business plan & used to deploy the quality policy
- (5.6.1) – Management review – General – records from management reviews shall be maintained
- (6.2.2.2) – Competence, training & awareness – maintain appropriate records of education, training, skills & experience
- (7.1) – Planning of product realization – records needed to provide evidence that the realization processes & resulting product meet requirements
- (7.2.2) – Review of requirements related to the product – records of the results of the review and actions arising from the review shall be maintained
- (7.2.2.2) – Organization manufacturing feasibility – The organization shall investigate, confirm & document the manufacturing feasibility of the proposed products in the contract review process, including risk analysis.
- (7.3.1) – Design & development planning – Note: design & development review, verification & validation have distinct purposes. They can be conducted & recorded separately or in any combination, as suitable for the product & the organization.
- (7.3.2) – Design & development inputs – inputs relating to product requirements shall be determined & records maintained
- (7.3.2.1) – Product design input – The organization shall identify, document & review the product design input requirements, including the following,Customer requirements (contract review) such as special characteristics, identification, traceability & packaging
- Use of information: the organization shall have a process to deploy information gained from previous design projects, competitor analysis, supplier feedback, internal input, field data, & other relevant sources, for current & future projects of a similar nature
- Targets for conformity to product requirements, life, reliability, durability, maintainability, timing & cost.
- (7.3.2.2) – Manufacturing process design input - The organization shall identify, document & review the manufacturing process design input requirements, including,Product design output data
- Targets for productivity, process capability & cost
- Customer requirements, if any
- Experience from previous developments
- (7.3.2.3) – Special characteristics – identify process control documents including drawings, FMEAs, control plans & operator instructions with the customer’s special characteristic symbol or the organisation’s equivalent symbol or notation to include those process steps that affects special characteristics
- (7.3.3.1) – Product design outputs – supplemental – The product design output shall be expressed in terms that can be verified & validated against product design input requirements. The product design output shall include,Design FMEA, reliability results,
- Product special characteristics & specification,
- Product error proofing, as appropriate,
- Product definition including drawings or mathematically based data
- Product design review results, and
- Diagnostic guidelines, where applicable.
- (7.3.3.2) – Manufacturing process design output – The manufacturing process design output shall be expressed in terms that can be verified against manufacturing process design input requirements and validated. The manufacturing process design output shall include,Specification and drawings,
- Manufacturing process flow chart / layout
- Manufacturing process FMEA,
- Control plan,
- Work instructions,
- Process approval acceptance criteria
- Data for quality, reliability, maintainability & measurability,
- Results of error proofing activities, as appropriate, and
- Methods of rapid detection & feedback of product/manufacturing process nonconformities.
- (7.3.4) – Design & development review – Records of the results of the reviews & any necessary actions shall be maintained.
- (7.3.5) – Design & development verification – Records of the results of the verification & any necessary actions shall be maintained.
- (7.3.6) – Design & development validation – Records of the results of validation & any necessary actions shall be maintained.
- (7.3.7) – Control of design & development changes – Design & development changes shall be identified & records maintained. Records of the results of the review of changes and any necessary actions shall be maintained.
- (7.4.1) – Purchasing process – Records of the results of evaluations & any necessary actions arising from the evaluation shall be maintained.
- (7.5.1.1) – Control plan – The organization shall develop control plans at the system, sub-system, component and/or material level for the product supplied including those for processes producing bulk materials as well as parts.
- (7.5.1.2) – Work instructions – The organization shall prepare documented work instructions for all employees having responsibilities for the operation of processes that impact conformity to product requirements (especially for for set-up personnel 7.5.1.3) (Instructions for rework, including re-inspection requirements 8.3.2).
- (7.5.1.4) – Preventive & predictive maintenance – Documenting, evaluating & improving maintenance objectives.
- (7.5.2) – Validation of processes for production & service provision – requirements for records (of validation & revalidation).
- (7.5.3) – Identification & traceability – Where traceability is a requirement, the organization shall control the unique identification of the product and maintain records.
- (7.5.4) – Customer property – If any customer property is lost, damaged, or otherwise found to be unsuitable for use, the organization shall report this to the customer & maintain records.
- (7.6) – Control of monitoring & measuring equipment – In addition the organization shall assess & record the validity of the previous measuring results when the equipment is found not to conform to requirements. Records of the results of calibration & verification shall be maintained.
- (7.6.2) – Calibration / verification records – Records of the calibration / verification activity for all gauges, measuring & test equipment, needed to provide evidence of conformity of product to determined requirements, including employee and customer –owned equipment, shall includeEquipment identification, including the measurement standard against which the equipment is calibrated
- Revisions following engineering changes
- Any out of specification readings as received for calibration/verification
- An assessment of the impact of out-of-specification condition
- Statements of conformity to specification after calibration / verification and
- Notification to the customer if suspect product or material has been shipped.
- (7.6.3.1) – Internal laboratory – The laboratory shall specify & implement, as a minimum, technical requirements for… (e)review of the related records
- (8.2.2) – Internal audit – Records of the audits & their results shall be maintained.
- (8.2.3.1) – Monitoring & measurement of manufacturing processes – >>The results of process studies shall be documented with specifications, where applicable, for means of production, measurement & test, & maintenance instructions. These documents shall include objectives for manufacturing process capability, reliability, maintainability & availability, as well as acceptance criteria. >>Significant process events, such as tool change or machine repair, shall be recorded. >>The organization shall record effective dates of process changes.
- (8.2.4) – Monitoring & measurement of product – Records shall indicate the person(s) authorizing release of product for delivery to the customer.
- (8.3) – Control of nonconforming product – Records of the nature of nonconformities & any subsequent actions taken, including concessions obtained shall be maintained.
- (8.3.4) – Customer waiver – The organization shall maintain a record of the expiration date or quantity authorized (concession or deviation permit).
- (8.5.2) – Corrective action – Records of the results of action taken.
- (8.5.2.4) – Rejected product/test analysis) – Records of these analyses shall be kept & made available upon request.
- (8.5.3) – Preventive action – Records of results of action taken.