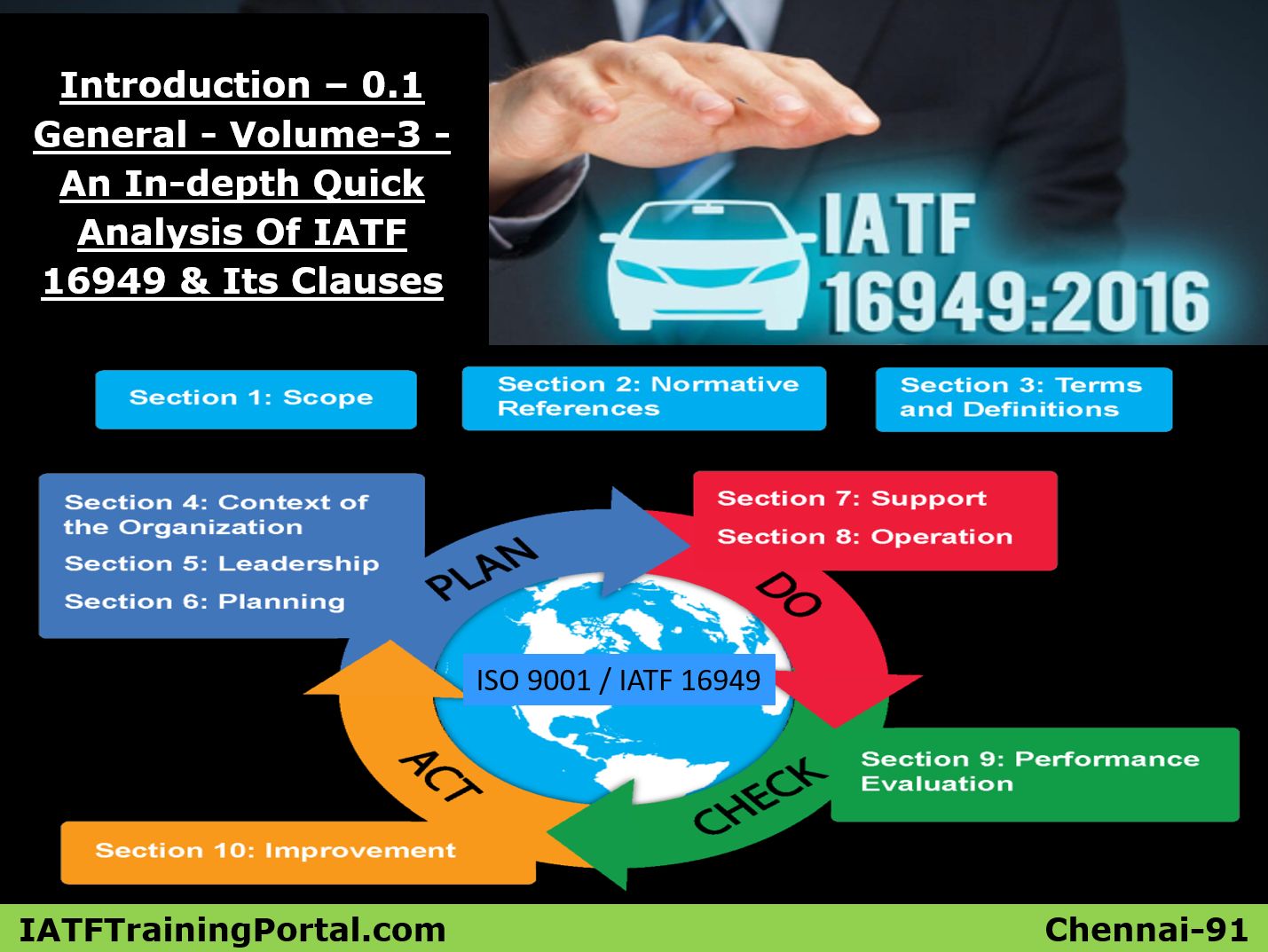
164 Must Read Glossary For TS16949 & Six Sigma Professionals
People who prepare for TS16949 IATF Auditor Evaluation process normally struggle w.r.t glossary terms, as these were spread at various places. Hence i have compiled all these glossary in one place in a word file.
Earlier i have uploaded these 164 glossaries as 45 pictures. These pictures can be quickly saved to your computers & inserted into powerpoint. You can use these powerpoint slides to train people. To see these images click this link "Go To 45 Image Slides"
164 Must Read Glossary
- 5.15 Vs 6 σGRR Multiplying Factor (MSA) - 5.15 represents 99% spread, 6 represents 99.73% spread.
2. Accredited laboratory (PPAP) – reviewed & approved by nationally recognized accreditation body, or as an alternative, a customer recognized accreditation body (conforming to ISO/IEC guide 58 of calibration or test laboratory accreditation to ISO/IEC 17025, or national equivalent).
3. Accuracy (MSA) - closeness of agreement between an observed value & the accepted reference value.
4. Active part (PPAP) – currently being supplied for original equipment or service applications.
5. Analysis of variance (MSA) – ANOVA (statistical method used in DOE)
6. Apparent resolution (MSA) - least increment on instrument
7. Appearance item (PPAP) – visible once the vehicle is completed.
8. Apportionment - Reliability apportionment (APQP) - assignment of reliability goals from system to sub-system in such a way that the whole system will have the required reliability.
9. Appraiser variation (MSA) - same part, same instrument, different operators
10. Approved (PPAP) – used in PPAP to mean that the parts, materials, & and/or related documentation meet all customer requirements.
11. Approved drawing (PPAP) – an engineering drawing signed by the engineer & released through customer’s system.
12. Approved materials (PPAP) – governed either by industry standard specifications or by customer specifications.
13. Approved source list (PPAP) – list of organizations & suppliers that have been found acceptable to the customer.
14. Attribute data (PPAP/SPC) – qualitative data that can be counted for recording & analysis.
15. Authorized customer representative(s) (PPAP) – is the individual or individuals having approval authority on behalf of the customer.
16. Autocorrelation (SPC) – degree of relationship between elements of a stationary time series
17. Average run length (SPC) – number of sample subgroups expected between out-of-control signals
18. Benchmark data (APQP) – to determine how best-in-class performance is achieved.
19. Between-subgroup variation (SPC) (See variation)
20. Bias (MSA) (also Accuracy, location) – [observed average – reference value]
21. Bill of material (APQP) – list of components / materials to manufacture a product.
22. Black box (PPAP) – refers to a part where design responsibility belongs to the organization or the supplier. ODD (outside design & development) has the equivalent meaning.
23. Bulk material (PPAP) – is a substance (non-dimensional solid, liquid, gas) such as adhesives, sealants, chemicals, coatings, fabrics, lubricants, etc.
24. Bulk materials requirements checklist (PPAP) – defines customer PPAP requirements for bulk material.
25. CAD/CAM math data (PPAP) – is a form of design record by which all dimensional information necessary to define a product is conveyed electronically.
26. Calibration (MSA) - set of operations that establish, under specified conditions, the relationship between a measuring device & a traceable standard of known reference value & uncertainty (PPAP) – is a set of operations which compares values taken from a piece of IMTE or a gage to a known standard under specified conditions.
27. Calibration interval (MSA) – specified amount of time or set of conditions between calibrations during which the calibration parameters of a measuring device are considered valid.
28. Capability (MSA) - combined variation of measurement errors (random & systematic) based on a short-term assessment of the measurement system….. (PPAP) – total range of inherent variation in a stable process.
-----1. Long term capability (MSA) - within-subgroup variation over a long period of time. This differs from performance as it does not include the between-subgroup variation.
-----2. Process capability (SPC) - six sigma range of inherent process variation
29. Cause & effect diagram (SPC) – Simple problem solving tool, uses graphic description to analyze sources of variation. Also called as fishbone (after its appearance) or Ishikawa (after its developer)
30. Centerline (SPC) – line representing average value
31. Characteristic (SPC) – a distinguishing feature (of a process or its output)
32. Characteristics matrix (APQP) – display relationship between process parameters Vs mfg. stations.
33. Checked print (PPAP) – is a released engineering drawing with actual measurement results recorded by the organization adjacent to each drawing dimension & other requirements.
34. Common cause (SPC) –source of inherent process variation, affects all outputs.
35. Confidence interval (MSA) - range of values expected to include the true value of a parameter…..(SPC) – An interval or range of values, calculated from sample data, that contains, with a (100-∞) degree of certainty, the population parameter of interest.
36. Conformance (PPAP) – part or material meets customer’s specifications & requirements.
37. Consecutive (SPC) – in succession
38. Continual improvement (SPC) – dynamic strategy contrasts with outgoing NCs are inevitable.
39. Control or Statistical control (PPAP / SPC) – all special causes eliminated.
-----1. In-control (MSA) - process with only common cause variation
-----2. Out of control (MSA) - process with chaotic, assignable, or special cause
-----3. Process control (SPC) – Condition describing a process from which the effect of all special causes of variation have been eliminated & only that due to common causes remain….. (MSA) purpose of measurement & decision criteria applies to real-time production to assess process stability & the measurand to natural process variation (result indicates either stable and “in-control” or “out-of-control”)
-----4. Statistical process control (SPC) – use of statistical techniques to attain statistical control.
40. Control chart (SPC / MSA/PPAP) – graphic representation of a characteristic of a process with a center line & one or two control limits.
-----1. ARMA control chart (SPC) – Auto Regressive Moving Average, used where sample data are independent is violated
-----2. CUSUM control chart (SPC) – to detect small to moderate shifts in the process average or variability. CUmulative SUM of deviations from the target & puts equal weight on the current & recent past data.
-----3. EWMA control chart (SPC) (Exponentially Weighted Moving Average) – to detect small shifts in process location.
-----4. MCUSUM control chart (SPC) – Multivariate CUmulative SUM – applying CUSUM to multivariate situations.
-----5. MEWMA control chart (SPC) – Multivariate Exponentially Weighted Moving Average.
-----6. Multivariate control chart (SPC) – for multivariate distribution.
-----7. Non-normal control chart (SPC) – adjustments made while compensating for the characteristics of a non-normal distribution.
-----8. Probability based charts (SPC) – uses categories data & probabilities related to the categories.
-----9. Regression control chart (SPC) – to determine if & when deviation from the known predictable relationship occurs.
-----10. Residuals control chart (SPC) – monitors using differences between a fitted model & the data.
-----11. Short run control chart (SPC) – adjusted for small volumes during a single run.
41. Control limit (SPC) – a line or lines on a control chart used as a basis for judging the stability of a process.
42. Control plans (PPAP) – written descriptions of the system for controlling production parts, bulk materials and processes.
43. Control statistic (SPC) – a value calculated from or based upon sample data.
44. Correlation (SPC) – degree of relationship between variables.
45. Correlation matrix (SPC) – a matrix of all possible correlations.
46. Customer (PPAP) – recipient of the organization’s or supplier’s product or service.
47. Data (MSA) – a collection of variable or discrete observations under a set of conditions.
48. Datum (SPC) – singular of “data”. A single point in a series of data.
49. Design for manufacturability & assembly (APQP) – optimizes relationship between design function, manufacturability & ease of assembly.
50. Design information checklist (APQP) – a mistake proofing checklist designed to assure that all important items were considered in establishing design requirements.
51. Design record (PPAP) – is the part drawing, specifications, and/or electronic (CAD) data used to convey information necessary to produce a product.
52. Design reviews (APQP) – milestone checkpoints to review progress proactively.
53. Design validation (APQP) – confirmation through objective evidence on intended use has been fulfilled.
54. Design verification (APQP) – confirmation through objective evidence, that specific requirements have been fulfilled.
55. Designed experiment (MSA) - changes made to process factors & the effects observed, to determine relationship of process variables
56. Design-intended robust range (PPAP) – limits within which parameters may be allowed to vary while still ensuring that a product complies with fitness for use.
57. Detection (SPC) – identify unacceptable after produced & separate.
58. Discrimination (MSA) - smallest readable unit or least count
59. Distinct data categories (MSA) - reliably distinguished, determined by effective resolution of the measurement system & part variation. ndc (MSA) (number of distinct categories) - [1.41(pv/grr)]
60. Distribution (SPC) – individual values as a group form a pattern. Described by Location (mean, median), spread (std.dev, range), shape (symmetry, peaked, skewed).
-----1. Binomial distribution (SPC) – a discrete probability distribution for attributes data (p, np chart).
-----2. Non-normal distribution (SPC) – does not follow the normal form (moments > order two are not all zero)
-----3. Normal distribution (SPC) - continuous, symmetrical & bell-shaped
-----4. Poisson distribution (SPC) - discrete probability distribution for attributes data (c, u control charts)
61. Durability (APQP) – probability that an item will continue to function at expected levels without overhaul or rebuild.
62. Effective resolution (MSA) - size of data category when total measurement system variation is considered
63. F ratio (MSA) - ratio of between-group mean square error to the within-group mean square error (used to assess the probability of random occurrence)
64. Failure mode & effects analysis (FMEA) (APQP / PPAP) – analytical methodology used to ensure potential problems have been considered & addressed throughout the product & process development (APQP)
65. Feasibility (APQP) – a determination of success w.r.t process, design, procedure or plan.
66. Gage R&R (MSA) - estimate of combined variation of repeatability & reproducibility (equal to sum of within-system & between-system variances).
67. Histogram (MSA) - frequency of grouped data
68. Independent & identically distributed (MSA) - homogeneous, independent & randomly distributed
69. Independent (MSA) - no effect between one event on the probability to another event
70. Individual (SPC) – single unit or single measurement normally denoted by “x”.
71. Interaction (MSA) – a combined effect or outcome resulting from two or more significant variables
72. Laboratory (PPAP) – test facility that may include chemical, metallurgical, dimensional, physical, electrical, reliability testing or test validation.
73. Laboratory scope (PPAP) – is a quality record containing,
-----§ Specific tests, evaluations & calibrations that an organization’s laboratory has the ability & competency to perform
-----§ List of equipment which it uses to perform the above
-----§ List of methods & standards to which it performs the above
74. Linearity (MSA) - change in bias over entire operating range
75. Location (SPC) – central tendency (mean, median, mode)
-----1. Average (SPC) Mean (SPC) – average of values (location)
-----2. Median (SPC) – middle value in a group when arranged from lowest to highest.
-----3. Mode (SPC) - most frequently occurring (there may be more than one mode)
-----4. Process average (SPC) (location, Xdoublebar) – overall average
76. Loss function (SPC) – customer sensitivity (loss) Vs deviations from the target (design intent).
77. Marked print (PPAP) – modified, signed & dated by the customer engineer.
78. Measurand (MSA) - defined set of specifications for a measurement application
79. Measurement system (MSA) - complete process used to obtain measurements
80. Measurement system error (MSA) - combined variation due to gage bias, repeatability, reproducibility, stability & linearity
81. Metrology (MSA) - science of measurement
82. Moving range (SPC) – adding the new point & deleting the oldest chronological point.
83. Nonconforming units (SPC) – units do not conform to a specification (p, np charts)
84. Nonconformity (SPC) – individual NC-unit can have more than one NC.
85. Non-replicable (MSA) - inability to make repeated measurements due to dynamic nature of the measurand
86. Operational definition (SPC) – a criterion, a test & a decision to an object or to a group.
87. Organizations (PPAP) – are providers of,
-----§ Production materials
-----§ Production or service parts
-----§ Assemblies or
-----§ Heat treating, welding, painting, plating or other finishing services
88. Over-adjustment (SPC) – tampering, taking action when a process is stable.
89. Packaging (APQP) – protection & containment with ease of handling.
90. Pareto chart (SPC) – ranking w.r.t cost or total variation.
91. Part submission warrant (PSW) (PPAP) - Warrant (PPAP) – is an industry standard document required for all newly-tooled or revised products in which the organization confirms that inspections & tests on production parts show conformance to customer requirements.
92. Part to part variation (MSA) - variation due to measuring different parts
93. Part variation (MSA) - part to part & time to time variation for a stable process
94. Pass through characteristics (APQP) – parts received from supplier used as it is (no modification or validation).
95. Performance (MSA) - combined variation of measurement errors (random & systematic) based on a long-term assessment of the measurement system
-----1. Process performance (SPC) - six sigma range of total process variation
96. Perishable tools (PPAP) – are drill bits, cutters, inserts, etc. used to produce a product & which are consumed in the process.
97. Point estimate (SPC) - single number, egs: average or standard deviations
98. Precision - repeatability (MSA) - expected variation of repeated measurements over the range of measurement
99. Pre-control (SPC) – probabilistic analysis to product control using two data points within each sample.
100. Prediction interval (SPC) – predicting interval once the regression model is established for a population.
101. Preliminary bill of material (APQP) – completed prior to design & print release.
102. Preliminary process flow chart (APQP) – early depiction of the anticipated mfg.process for a product.
103. Prevention (SPC) – a pro-active strategy directing analysis & action toward correcting the process itself.
104. Probability (MSA) - estimate describing the chance a specific event will occur, probability estimates range between 0-impossible to 1-sure
105. Problem solving (SPC) - symptoms to causes, causes to actions
106. Process (PPAP) – set of interrelated or interacting activities which transform inputs into outputs….. (SPC) – combination of 6Ms to produce output (product r process)
107. Process flow diagram (PPAP) – is a schematic representation of the process flow.
108. Product assurance plan (APQP) – A part of product quality plan. It is a prevention oriented management tool that addresses product design, process design, & when applicable software design.
109. Product control (MSA) - assess measurand to a specification (result is either “in-tolerance” or “out-of-tolerance”)
110. Production environment (PPAP) – all of the process conditions surrounding or affecting the manufacture & quality of a part or product.
111. Production material (PPAP) – material which has been issued a production part number by the customer & is shipped directly to the customer.
112. Production part (PPAP) – manufactured at the production site using production tooling, gaging, process, materials, operators, environment, & process settings (eg.: feeds speed cycle times pressures temperatures)
113. Production part approval submission (PPAP) – specific quantities taken from significant production run made in production environment submitted for approval.
114. Production rate (PPAP) – is the agreed upon no. of parts produced in a planned time period to meet customer assembly or mfg. plant production volume requirements (with consideration of other product mix & machine availability).
115. Quadratic (SPC) - second order mathematical model (egs: parabola).
116. Quality indices (PPAP) – measures of capability or performance for either product or process.
117. Quality planning (PPAP) – structured process for defining methods (measurements, tests) that will be used in the production of a specific product or family of products. Embodies the concepts of defect prevention & continual improvement as contrasted with defect detention.
118. Quality planning approval (APQP) – a review & verification that all planned controls & processes are being followed.
119. Quality record (PPAP) – is a document stating results achieved or providing evidence of activities performed.
120. Randomness (SPC) - a condition in which no pattern in the data can be discerned.
121. Rational subgroup (SPC) – to give maximum chance in each subgroup to be alike & subgroups to differ one from the other.
122. Reference value (MSA) - master value
123. Regression analysis (MSA) - mathematical relationship between two or more variables
124. Regular production tooling (PPAP) – tooling with which the manufacturer intends to produce production product.
125. Reliability (APQP) – the probability that an item will continue to function at customer expectation levels at a measurement point, under specified environmental & duty cycle conditions.
126. Repeatability (MSA) - fixed part, instrument, standard method, operator, environment, & assumptions (referring as “Equipment Variation” (EV) is misleading, best term is within-system variation)
127. Replicable (MSA) - the ability to make repeated measurements on the same sample where there is no significant physical change to the measurand or measurement environment
128. Replication (MSA) - multiple trials under identical conditions
129. Reproducibility (MSA) - same part, same instrument, different operators (average variation between-systems or between-conditions of measurement)
130. Resolution (MSA) (measurement resolution or effective resolution) - capability of the measurement system to detect & faithfully indicate even small changes of the measured characteristic
131. Run (SPC) - consecutive points increasing or decreasing or above or below centerline
132. Saleable product/part (PPAP) – specified on the contract between the customer & organization.
133. Sample (SPC) (see subgroup)
-----1. Convenience sampling (SPC) - easy to collect samples. (Egs: before a break period, top of a container)
-----2. Haphazard sampling (SPC) - unsystematic, indiscriminant, unplanned, chaotic
-----3. Random sampling - Probability sampling (SPC) - every sample point has same chance of being selected.
134. Scatter diagram (MSA) – (x-y) plot to assess relationship between two variables)
135. Sensitivity (MSA) - smallest input signal that results in a detectable output signal for a measurement device
136. Shape (SPC) - overall pattern formed by a distribution of values (egs: skew, kurtosis)
137. Sigma (σ) (SPC) - greek letter used to denote std.dev of a population.
138. Significance level (MSA) - statistical level selected to test the probability of random outcomes, also associated with risk (decision error)
139. Significant production run (APQP) – product made using all production tools, processes, equipment, environment, facility & cycle time. (PPAP) – see PPAP 2.1
140. Simulation (APQP) – imitating some or all the behavior of one system with a different, dissimilar system.
141. Site (PPAP) – location at which value added manufacturing processes occur.
142. Special cause (SPC) - often intermittent & unpredictable, affects only some of the outputs. Signaled by one or more points beyond control limits or non-random pattern of points within control limits.
143. Special characteristics (APQP) – characteristics having significant impact on the quality, function, fit, safety – designated by customer or selected by organization through knowledge of product & process….. (PPAP) – Product or process parameters which can affect safety or compliance with regulations, fit, function, performance or subsequent processing of a product.
144. Specification - Tolerance (SPC) (bilateral, unilateral) - engg reqmt for judging acceptability of a particular characteristic….. (PPAP) – document stating requirements. - allowable deviation from a nominal value that maintains fit, form & function
145. Spread (SPC) - expected span of values from smallest to largest in a distribution.
-----1. Process spread (SPC) - Dispersion (SPC) (Moving range chart) – often shown as average plus or minus some number of standard deviations.
-----2. Std. deviation (SPC) - measure of the spread of the process output.
-----3. Range (SPC) – (Highest – lowest), measure of process spread.
146. Stability (MSA) - change in bias over time..... Stability (SPC) - no special causes, property of being in statistical control.
147. Stable process (SPC / PPAP) - process in statistical control.
148. Statistic (SPC) - a value calculated from sample data used to make inferences about the process that produced the output.
149. Statistical inference (SPC) - single number (point estimate) or a pair of numbers (interval estimate)
150. Statistical tolerance limits (SPC) – interval or range expected to contain a specified proportion of a population.
151. Submission level (PPAP) – refers to level of evidence required for PPAP submission.
152. Subsystem (APQP) – a major part of a system which itself has the characteristics of a system, usually consisting of several components or processes.
153. Suppliers (PPAP) – Providers of production materials or production or service parts.
154. System (APQP) – a combination of several components, processes or pieces of equipment integrated to perform a specific function.
155. Team feasibility commitment (APQP) – team commitment on manufacturability & delivery of a product at required rate & cost.
156. Timing plan (APQP) – listing of tasks, assignments, events & timing required to provide a product that meets customer needs & expectations.
157. Tool (PPAP) – used in process machinery to transform raw material into finished part or assembly.
158. Uncertainty (MSA) - quantified expression of measurement reliability (range assigned to a measurement result that describes, within a defined level of confidence, the limits expected to contain the true measurement result).
159. Unimodal (MSA) - contiguous group of data that has one mode
160. Validation (PPAP) – confirmation through objective evidence that the requirements for a specific intended use or application have been fulfilled.
161. Variables data (PPAP) – quantitative data
162. Variation (SPC) – Inevitable differences among individual outputs of a process
-----1. Inherent variation (SPC) – Due to common cause only
-----2. Within-subgroup variation (SPC) – Due to within-subgroups. If the process is in statistical control, this variation is a good estimate of the inherent process variation. Can be estimated from control charts by Rbar/d2 or sbar/c4.
-----3. Between-subgroup variation (SPC) – Due to between-subgroup. If the process is in statistical control, this variation should be zero.
-----4. Total process variation (SPC) – Variation due to both within-subgroup & between-subgroup.
163. Verification (PPAP) – confirmation through objective evidence that specific requirements have been fulfilled.
164. Voice of the customer (APQP) – Positive & negative feedback of customers including likes, dislikes, problems & suggestions.